What is a seafood feed mill within the seafood supply chain?
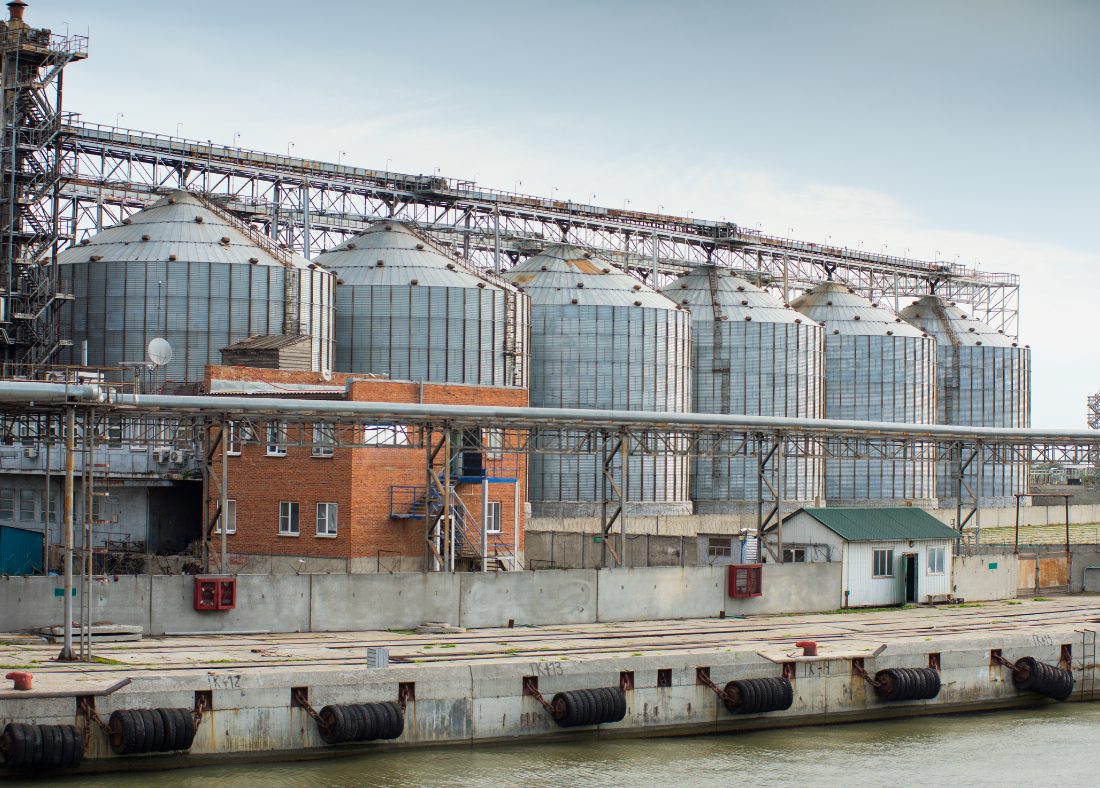 Note: Each step in the seafood production chain has its own importance, but they work together to create the best quality products for consumers. In the #SeafoodWithStandards campaign, throughout 2022 we will be highlighting each stop along the production chain to pull back the curtain and explain what happens there. The next stop is seafood feed mills, which contribute/connect to both hatcheries and farms along the seafood supply chain.
Note: Each step in the seafood production chain has its own importance, but they work together to create the best quality products for consumers. In the #SeafoodWithStandards campaign, throughout 2022 we will be highlighting each stop along the production chain to pull back the curtain and explain what happens there. The next stop is seafood feed mills, which contribute/connect to both hatcheries and farms along the seafood supply chain.
What is a seafood feed mill?
Feed mills are responsible for the production of animal feeds, including those consumed by aquaculture facilities, livestock and poultry animals, and companion animals. For aquaculture, manufactured feeds provide aquatic animals with optimally formulated feeds to meet all nutrient requirements for optimal growth and performance. These manufactured feeds are specifically formulated to ensure that the animal receives optimal nutrients for each life stage.
Optimal nutrition is important for preventing deficiencies, malnutrition, and disease. In addition to providing aquatic animals with nutrient-dense feeds, feed mills can also be responsible for the manufacture of pet foods for companion animals, including cats and dogs. Although the finished animal feeds can vary greatly between livestock and companion animals, most are generally produced from similar ingredients. These ingredients are derived from plant-based grains and animal-based cuts and by-products. To help ensure the safety of animal food from biological hazards, the implementation of a feed mill biosecurity plan is essential.
What happens at feed mills?
As there is huge variety in species and their nutrition needs of seafood worldwide, there is no uniform procedure for formulating fish feed. However, there is a general flow of operations that happens at most feed mills.
The priority of a seafood feed mill is to create feed for fish that is nutritionally powerful as well as being optimally suited to meet the needs of the aquatic environments on fish farms.
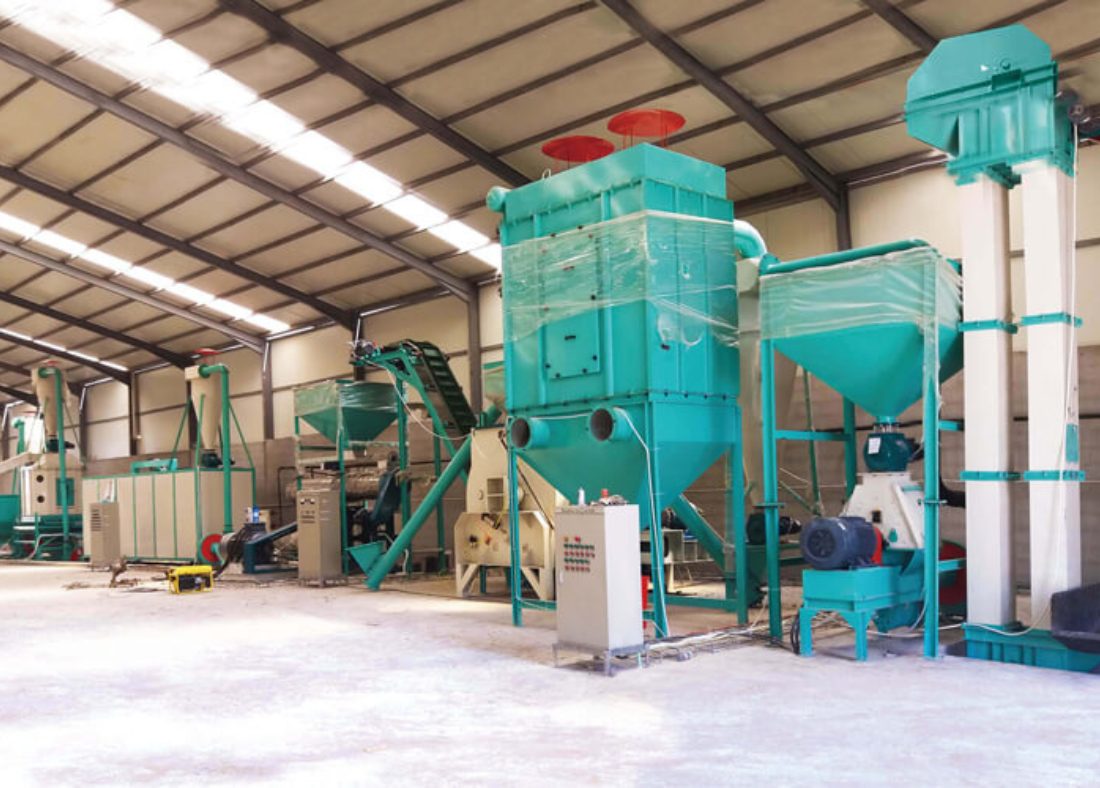

Steps of production at seafood feed mills include:
- Ingredient sourcing
- Feed formulation
- Manufacturing
- Dispatching
- Transporting
Once the fish feed has been manufactured, it is then sent on to hatcheries and farms, which then lead into processing plants and finally, retail and food service for eventual consumption.
Why are feed mills important?
Without seafood feed mills working to increase the nutritional value in the diets of farmed aquatic animals, it is possible that the farmed species would not be as nutritionally valuable to the end consumer, and it’s also possible the species would have greater disease outbreaks, which means decreased food safety.
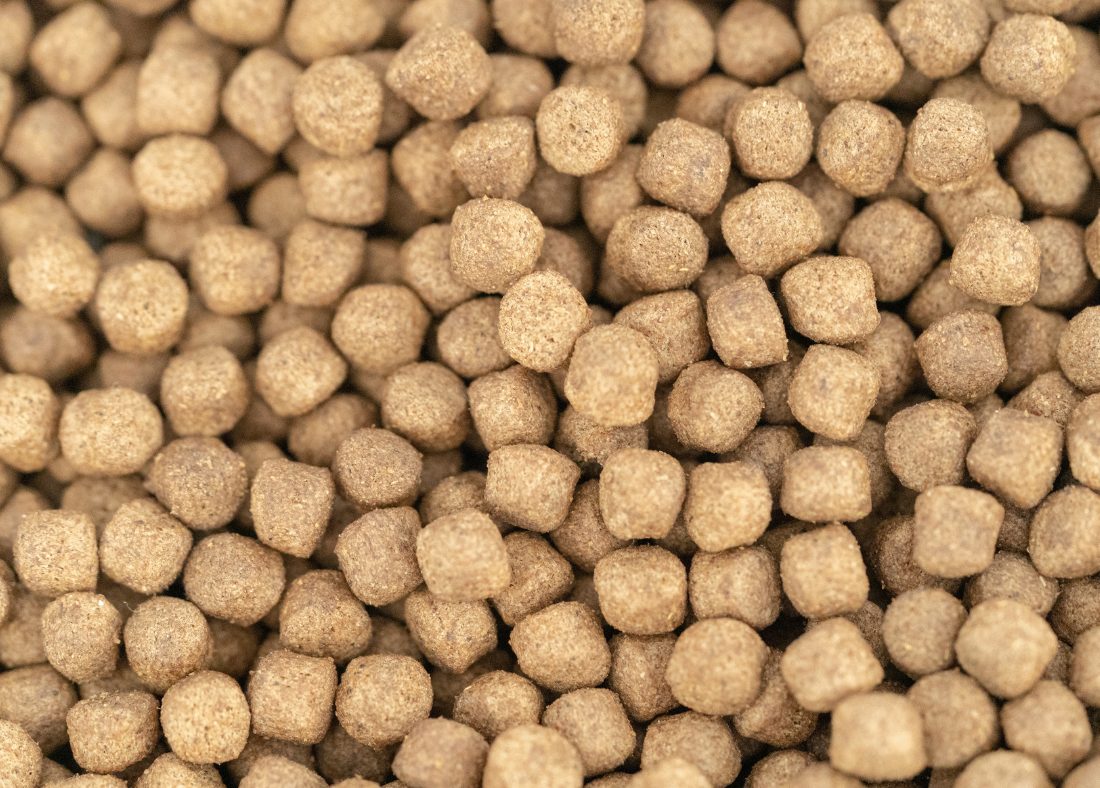 Decades, if not longer, of research and trial and error, have gone into formulating the most optimum ingredients for fish feed. Scientists and farmers alike have honed in on which ingredients ensure that each species thrives in its farming environment.
Decades, if not longer, of research and trial and error, have gone into formulating the most optimum ingredients for fish feed. Scientists and farmers alike have honed in on which ingredients ensure that each species thrives in its farming environment.
GSA’s Feed Mill Standard
Third-party certification programs that have standards for seafood production ensure that responsible practices are being used with regard to the workers, the animals, and the environment. As part of GSA, Best Aquaculture Practices (BAP) ensures aquaculture is performed responsibly through its third-party certification program. BAP is the only seafood-specific certification program that certifies every step in the production chain (other programs only certify certain stops along the chain).
The BAP Feed Mill Standard is the only seafood-specific feed mill standard and is compliant with the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI) and the Global Social Compliance Programme (GSCP).
The Feed Mill Standard upholds the pillars of responsible seafood. The standard provides clarity on responsible production as it pertains to ingredient sourcing, feed formulation, and manufacturing. Note: the animal health and welfare pillar of responsible seafood does not pertain to feed mills, so this pillar is not part of the Feed Mill Standard.
How does the feed mill standard cover the pillars of responsible seafood?
Food Safety
 Food safety refers to the handling, preparing, and storing of food in a way that reduces the risk of people getting sick. With any food production, there are always food safety hazards to consider.
Food safety refers to the handling, preparing, and storing of food in a way that reduces the risk of people getting sick. With any food production, there are always food safety hazards to consider.
Some of the food safety requirements include:
- Having a plan in place to address food safety hazards and the adoption of appropriate process controls
- Conducting routine cleaning operations
- Using appropriate equipment for transport, storage, handling, etc.
- Conducting periodic sampling of feed ingredients
- Having pathogen control procedures in place
Social Accountability
 The social accountability requirements in the Feed Mill Standard ensure producers are following best practices with regard to human rights, labor laws, and employee health and safety.
The social accountability requirements in the Feed Mill Standard ensure producers are following best practices with regard to human rights, labor laws, and employee health and safety.
The social accountability requirements in the Feed Mill Standard include:
- Ensuring workers are paid appropriately and provided benefits that are, at minimum, required by local or national law
- Compensating workers for overtime hours worked beyond the mandated work week
- Not engaging in the use of forced, indentured, bonded, or child labor
- Providing equal opportunity with respect to recruitment, hiring, terms of employment, compensation, promotion, etc.
- Providing safe, healthy, and clean conditions in all work, rest, dining, and where applicable, housing areas
Environmental Responsibility
 The environmental responsibility pillar ensures feed mills are using best practices that protect the environment.
The environmental responsibility pillar ensures feed mills are using best practices that protect the environment.
The environmental responsibility requirements in the Feed Mill Standard include:
- Not sourcing raw material from illegal, unreported, or unregulated (IUU) fisheries, or by-products from such fisheries
- Developing and implementing a clear, written Plan of Action defining policies for responsibly sourcing fishmeal and fish oil from reduction fisheries and setting clear goals for responsibly sourcing soy ingredients
- Proper labeling, storage, and disposal of chemicals
- Proper disposal of waste materials
View the full What happens at seafood feed mills? infographic.





