
Improving salinity tolerance in tilapia
Salinity tolerance in tilapia can be improved by optimizing acclimation protocols, adding salt to the diet or hybridization between fast-growing and salt-tolerant species.
Early Mortality Syndrome is a new disease that has been detected at shrimp farms in Asia. It appears within 30 days of stocking and causes symptoms that include lethargy; soft, darkened shells and mottling of the carapace.

Salinity tolerance in tilapia can be improved by optimizing acclimation protocols, adding salt to the diet or hybridization between fast-growing and salt-tolerant species.

Shrimp exposed to high concentrations of nitrate exhibit shorter antennae, gill abnormalities and hepatopancreas lesions. Nitrate toxicity is more of an issue for shrimp raised in lower-salinity waters.

With a hatchery system that involves collection of eggs and larvae, and hormonal sex reversal, it is possible to produce billions of monosex tilapia (all-male) fry to satisfy demand and accelerate aquaculture development.

Taurine may not only improve growth and performance, but also is required to reduce nutritional diseases such as green liver disease and low hematocrit levels in some fish.
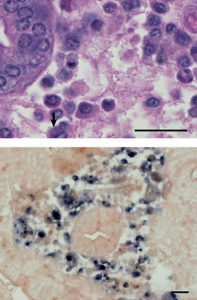
An in situ hybridization procedure can be used to diagnose blue crabs from Chesapeake Bay infected with a reovirus.

Poultry byproduct meal can replace much of the fishmeal in shrimp diets. To better understand the nutritive value of its fat, the authors analyzed the fat components and conducted a feeding trial.

Necrotizing hepatopancreatitis is a disease of shrimp that causes slow growth, low survival and poor feed conversion. Wet mount analysis is commonly used to diagnose NHP in ponds in Brazil.

To develop probiotics for marine shrimp, authors chose a bacterium with high growth velocity and great capacity to inhibit pathogens, among other traits.

Although carbon dioxide is not highly toxic, high levels in the blood have many negative physiological consequences. As carbon dioxide increases, higher dissolved oxygen tension is necessary to load hemoglobin with oxygen.
Key to avoiding the cyclical rise and fall of production and prices is the move toward controlled reproduction of shrimp to perform within the structure chosen, whether that is disease coping or disease avoidance.

To evaluate the value of incorporating tail weight and yield in shrimp-breeding programs, the authors carried out a study to estimate heritabilities and genetic correlations for the traits.

Achieving higher growth rates in shrimp can reduce risks, cut costs and increase economic opportunities. The amount of additional growth that is achievable is related primarily to shrimp genetics.

China’s expansive tilapia culture industry is based on exotic species introduced continuously since 1956. Technical advances for improving the limited germplasm are expected to aid the industry.

Floating closed-containment systems incorporate low-pressure pumping, oxygen supplementation, solid-waste separation and efficient feed management.

Cholesterol is an essential nutrient for penaeid shrimp. Trials found that a digestibility enhancer based on natural emulsifiers was as effective as purified cholesterol in improving shrimp growth and feed conversion.