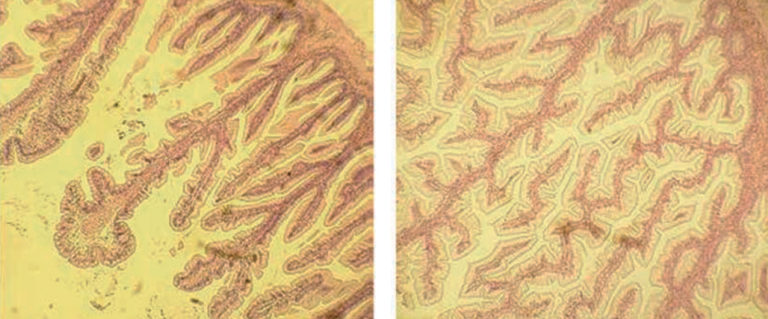
Protein digestive capacity correlated with nutrient presence, availability in shrimp feeds
Shrimp diets need amino acid composition, balance and availability. Protein digestive capacity appears related to both nutrient availability and composition in feed.