
Coastal aquaculture supports varied systems in Haiphong
Haiphong province is one of the main shrimp culture areas in northern Vietnam. Its climate is influenced by two monsoon regimes.
Snook are indigenous to coastal waters from Florida, USA, to Brazil. Mote Marine Laboratory has spawned snook for stock enhancement research.

Haiphong province is one of the main shrimp culture areas in northern Vietnam. Its climate is influenced by two monsoon regimes.

One catfish species of the genus Pangasius, commonly known as the basa catfish, has proven very adaptable for intensive production.

Pulsed light appears to kill all types of bacteria and eukaryotic microorganisms with equal effectiveness and could be a cost-effective control method.

The Australian red claw crayfish is a large freshwater crayfish native to northern Australia and the catchments of southeastern Papua New Guinea.

Amberjacks have excellent aquaculture potential due to their adaptability to conditions of intensive culture, extremely fast growth, and high market value.

Research at the Achotines Laboratory on the southern tip of the Azuero Peninsula of Panama centers on larval tuna biology.

The objective is to demonstrate that cobia can be successfully raised in the Bahamas using advanced offshore technology with low impact and high yield.

Research in Japan and Korea over the past decade or two has resulted in Pacific cod production in Japan and strong interest in Korea.

Amberjack, known as kahala in Hawaii, is a popular food fish that can accumulate naturally occurring ciguatera toxin by eating certain types of reef fish.
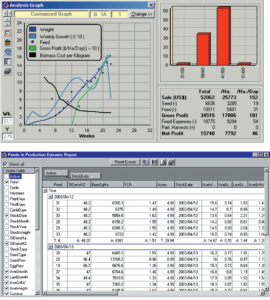
Powerful management tools like decision support systems can help shrimp producers improve their data collection and analysis to maximize cost efficiency.

One shellfish species commonly raised in the northeastern United States is the quahog or hard clam (Mercenaria mercenaria).

An assessment of the effects of smoking techniques on fillets of Nile tilapia, measuring yield, organoleptic qualities, composition, salt content and texture.

The authors studied the performance and economics of tilapia cage culture in southeast Brazil to evaluate the influence of different stocking densities.

Tilapia has aptly been called the “aquatic chicken,” a description that has become more accurate as time goes by. It is now the most widely cultured fish on the planet.

Tilapia are a diverse group of tropical fish with over 100 species that originally came from Africa and the Middle East but now are farmed worldwide.