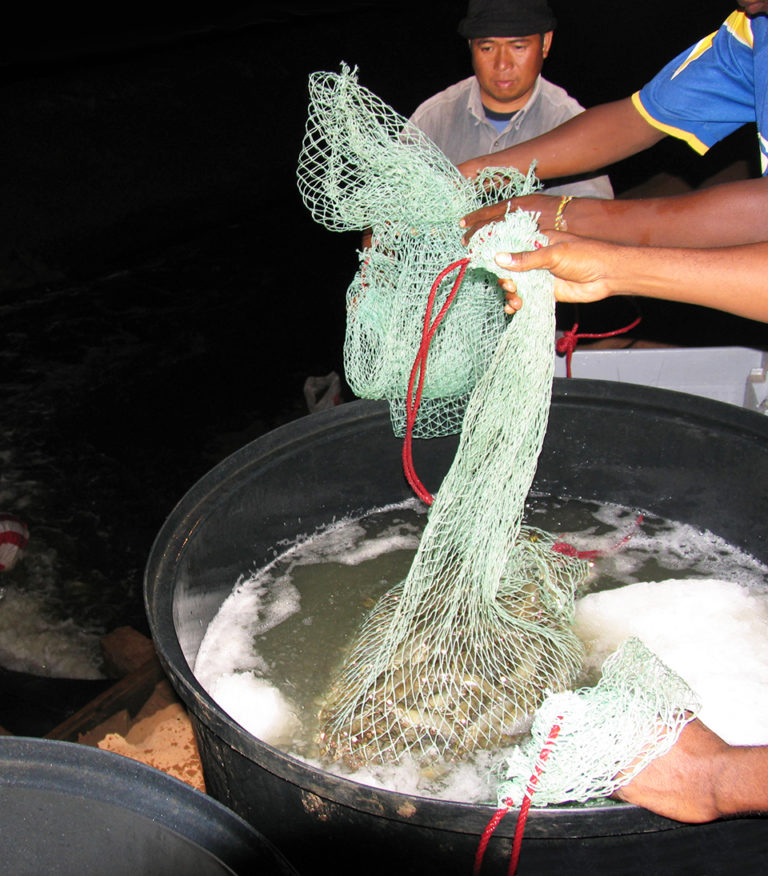
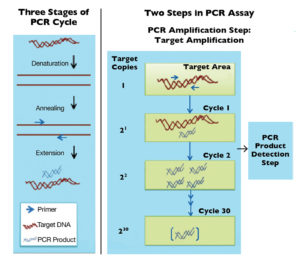
Salinity tolerance of Gulf corvina, prospective aquaculture species
After six weeks of experimental culture, comparable growth and survival were recorded in juvenile Gulf corvina raised at salinities of 5, 15, 25 or 35 ppt. Coupled with stable plasma osmolality values observed in fish at the varied salinities, these results confirmed the euryhaline nature of this species, a trait that could enhance its status as a candidate for aquaculture.