
Zero-exchange demonstration posts good results in Nicaragua
The Nicaragua Small Shrimp Producer Assistance Program built a closed, zero water-exchange shrimp production system to demonstrate the concepts and practices.
During the 1970s and 1980s, Ecuador's shrimp industry relied almost entirely on wild postlarvae but has since developed large hatcheries.

The Nicaragua Small Shrimp Producer Assistance Program built a closed, zero water-exchange shrimp production system to demonstrate the concepts and practices.
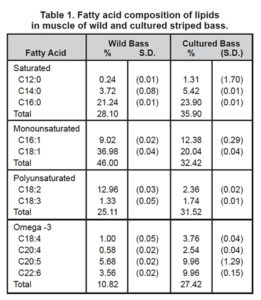
Studies comparing the differences between farmed and wild fish lipid profiles have been conducted, but there is no standard format for reporting.

Sexual growth dimorphism occurs in cultured aquatic species like tilapia, catfish and salmon, and has also been reported for cultured crustaceans.

Catfish feeds used in trials at LSU were formulated to possess an amino acid balance similar to that of the channel catfish body.

Commercial experience and research have demonstrated that phosphates can enhance sensory quality and increase consumer appeal for shrimp. Through over 10 years of research with shrimp from around the world, the Aquatic Food Products Lab at the University of Florida in Gainesville, Florida, USA has shown that consumers prefer shrimp properly treated with phosphates. However, processors must have a clear understanding that misuse of these ingredients can result in poor appearance, poor texture, and consumer rejection.

EU markets have special requirements for head-on shrimp. Organoleptic criteria are evaluated, including firmness of shell and head, malformations and color.
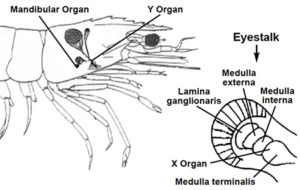
In most decapod crustaceans the physiological processes of metamorphosis, molting and reproduction are inextricably linked and controlled by hormones.

Rotifers are a dominant zooplankton that are a preferred prey for larval fish and one of the live feeds most often used by fish culturists.

The use of refrigerated freshwater algal paste for production of rotifers results in live feed with adequate nutritional properties for marine larviculture.

Dip shrimp in a 5 percent sodium bisulfite solution for 2 to 5 minutes to produce a bisulfite concentration of 30 to 50 ppm sulfur dioxide equivalent in the shrimp.
After numerous modifications during experiments with the freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii), a successful microbound diet has been developed.

Consideration of the effect of animal density usually does not include the critically important contribution of pathogen concentration to the dynamics of disease outbreaks.
Research with sockeye salmon fry in Washington state demonstrates that bioencapsulated artemia can deliver therapeutic erythromycin more efficiently than pelleted feeds.

In intensive fish hatcheries, successful larval rearing depends upon meeting larval metabolic demands with continuous feeding.

A study of hybrid tilapia breeding represents the minimum scale needed for achieving successful, in-house selective breeding.