
Shrimp breeding for resistance to Taura Syndrome Virus
In response to Taura Syndrome Virus outbreaks, the U.S. Marine Shrimp Farming Program initiated a selective-breeding program to improve resistance in Pacific white shrimp.
The Maricultura del Pacífico hatchery in Mexico uses two-stage selection that controls the pedigree of every animal to minimize inbreeding.

In response to Taura Syndrome Virus outbreaks, the U.S. Marine Shrimp Farming Program initiated a selective-breeding program to improve resistance in Pacific white shrimp.

Sandfish, a high-value sea cucumber, supports the aquaculture of other fish species by cleaning up waste on the bottoms of ponds or sea cages.

A rapid PCR assay for detection of WSSV was based on the nested, two-step PCR procedure recommended in the Manual of Diagnostic Tests for Aquatic Animals.

Mexico has a wide diversity of areas and water temperatures that are suitable for a variety of aquaculture species.

Nitrifying bacteria readily form biofilms on surfaces, and colonization by these important bacteria on the interior walls of RAS production units likely provides an additional source of nitrification.

Greece’s mussel aquaculture combines traditional hanging park culture with newer long-line methods. The traditional farms are generally family-run operations located in shallow, near-shore waters.

Studies by the author demonstrated that until morning D.O. concentrations fell below 3.0 mg/L, feed consumption of channel catfish was not affected.

Large-scale Gracilaria cultivation can be an effective means of improving water quality and promoting a more sustainable mariculture industry in China.

Blue shrimp are very similar to Pacific white shrimp, and can be raised under similar conditions. Blues grow faster and tolerate lower water temperatures.

The low-cost, low-infrastructure nature of OCAT open-ocean cage systems allows fish farmers to move from protected bay and harbor sites to more exposed locations that offer better water quality.

A study examined the replacement of poultry byproduct meal with plant proteins and low levels of squid meal in shrimp feeds. Production results for shrimp raised in ponds showed no significant difference in final weight, yield, FCR and survival among the four treatments with varied levels of poultry meal.

Intensive nursery systems are an extension of hatcheries to acclimate postlarvae to farm conditions and assess quality and health prior to pond stocking.
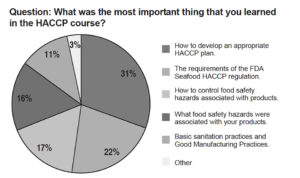
Seafood was one of the first U.S. commodities to be placed under the FDA's mandatory Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) regulations.

Trial demonstrated that inland shrimp farming with Pacific white shrimp in Sonora, Mexico, is a viable alternative for the use of groundwater where agriculture has been eliminated by the salinity in the aquifers.

Maintaining a favorable gut microflora in shrimp can help minimize the impacts of diseases and maximize digestive efficiency. Phytobiotic feed additives modulate microflora in shrimp toward a composition that favors beneficial bacteria and inhibits pathogenic microorganisms.