
Dietary threonine factor in tilapia fillet yield
In a commercial field trial, Nile tilapia were distributed in net cages and fed diets containing increasing threonine:lysine ratios.
In trials, a culture diet that naturally enhances rotifers and eliminates the need for enrichment was tested. Skretting feed specialists found similar growth and reproduction figures were registered with a conventional rotifer enrichment diet and a standalone diet for a period of nine weeks.

In a commercial field trial, Nile tilapia were distributed in net cages and fed diets containing increasing threonine:lysine ratios.

Field trails in Alabama, USA, demonstrated the potential of raising striped mullet with Pacific white shrimp in inland ponds. Using wild-caught fingerlings at low density, the trials found the same survival rates as for mullet and shrimp grown separately.

The culture of many marine fish species requires the concurrent culture of live feed such as algae and microcrustaceans. The addition of copepods to first feeding often improves survival for small-mouthed species.
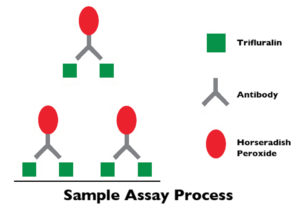
Antibody-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) tests are proven, sensitive, high-throughput alternatives to more costly and complex test methods for the detection of herbicide residues and other chemicals.

Probiotics can provide needed micronutrients that prime immune responses in larval fish, thus increasing their survival in culture. Probiotic dosing can be applied via immersion, microcosm approaches and enrichment of live and formulated feeds.

Scientists have been working to understand cobia’s nutritional requirements and advance the economic and environmental sustainability of feeding carnivorous fish using fishmeal alternatives.

Based on the results of a study in Peru, the authors found that the high volumes of quick lime and hydrated lime needed to effectively control vibriosis outbreaks in shrimp ponds would raise pH levels in culture water and stress the animals under culture.

The presence of compounds such as geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol (MIB) in recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS) can result in earthy or musty off-flavors in salmonids raised in the systems.

After rapid expansion of glass eel culture in the mid-1990s was followed by overproduction, pricing problems, glass eel shortages and NGO pressures, European Union countries adopted national management plans for the eels. Importation of consumption eels was stopped, and exportation was phased out.

The ideal pH for most aquaculture species is between 6.0 and 8.5. Lower pH values may result in decreased growth and survival, and greater susceptibility to disease. pH typically is lowest in the early morning, increases during the afternoon and declines at night.

At present, Macrobrachium rosenbergii is the only shrimp species commercially farmed in Brazil. Most freshwater prawn farms are small, and prawn culture is often a secondary farming activity.

In trials raising larger juvenile shrimp than those used previously in indoor super-intensive recirculating raceway systems, the positive effects from increased stocking size, growth rate and survival resulted in a reduced crop duration time.

The authors conducted research to determine the optimum dietary protein levels and protein:energy ratios for different age groups of olive flounders.

In 2012, samples collected from 92 AHPNS-affected ponds in the Mekong Delta found a number of Vibrio isolates, with the majority V. parahaemolyticus.
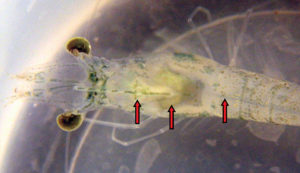
The University of Arizona Aquaculture Pathology Laboratory identifies a unique strain of Vibrio bacteria as the causative agent for EMS/AHPNS.