New artificial intelligence monitoring tool is ‘remarkably adept’ at identifying and counting fish species

As it stands, fisheries managers in British Columbia and beyond can’t track salmon returns in real-time. However, a groundbreaking new technology dubbed “Salmon Vision” could change that.
The technology combines artificial intelligence (AI) with age-old fishing weir technology. Early assessments show it to be remarkably adept at identifying and counting fish species, potentially enabling real-time salmon population monitoring for fisheries managers. Scientists and natural resource managers from First Nations, governments, academic institutions and conservation organizations published the first results of a unique salmon population monitoring tool in Frontiers in Marine Science.
“In recent years, we’ve seen the promise of underwater video technology to help us literally see salmon return to rivers,” said Dr. Will Atlas, lead author and Senior Watershed Scientist with the Portland-based Wild Salmon Center. “That dovetails with what many of our First Nations partners are telling us: that we need to automate fish counting to make informed decisions while salmon are still running.”
The Salmon Vision pilot study annotates more than 500,000 individual video frames captured at two Indigenous-run fish counting weirs on the Kitwanga and Bear Rivers of B.C.’s Central Coast. The first-of-its-kind deep learning computer model, developed in data partnership with the Gitanyow Fisheries Authority and Skeena Fisheries Commission, shows promising accuracy in identifying salmon species. It yielded mean average precision rates of 67.6 percent in tracking 12 different fish species passing through custom fish-counting boxes at the two weirs, with scores surpassing 90 and 80 percent for coho and sockeye salmon: two of the principal fish species targeted by First Nations, commercial and recreational fishers.
“When we envisioned providing fast grants for projects focused on Indigenous futurism and climate resilience, this is the type of project that we hoped would come our way,” said Dr. Keolu Fox, a professor at the University of California-San Diego, and one of several reviewers in an early crowdfunding round for the development of Salmon Vision.
Real-time data on salmon returns is critical on several fronts. According to Atlas, many fisheries in British Columbia have been data-poor for decades. That leaves fisheries managers to base harvest numbers on early season catch data, rather than the true number of salmon returning. Meanwhile, changing weather patterns, stream flows and ocean conditions are creating more variable salmon returns: uncertainty that compounds the ongoing risks of overfishing already-vulnerable populations.
“Without real-time data on salmon returns, it’s extremely difficult to build climate-smart, responsive fisheries,” said Dr. Atlas. “Salmon Vision data collection and analysis can fill that information gap.”
Atlas said the tool will be “invaluable” to First Nation fisheries managers and other organizations both at the decision-making table – in providing better information to manage conservation risks and fishing opportunities – and in remote rivers across salmon country, where on-the-ground data collection is challenging and costly.
The next step is to expand the model with partner First Nations into a half-dozen new watersheds on B.C.’s North and Central Coast. The Salmon Vision team is implementing automated counting on a trial basis in several rivers around the B.C. North and Central Coasts in 2023. The goal is to provide reliable real-time count data by 2024.
Now that you've reached the end of the article ...
… please consider supporting GSA’s mission to advance responsible seafood practices through education, advocacy and third-party assurances. The Advocate aims to document the evolution of responsible seafood practices and share the expansive knowledge of our vast network of contributors.
By becoming a Global Seafood Alliance member, you’re ensuring that all of the pre-competitive work we do through member benefits, resources and events can continue. Individual membership costs just $50 a year.
Not a GSA member? Join us.
Author
-
Responsible Seafood Advocate
[103,114,111,46,100,111,111,102,97,101,115,108,97,98,111,108,103,64,114,111,116,105,100,101]
Related Posts

Intelligence
Artificial intelligence successfully predicts toxic algae in UK seafood
Molecular biology-based approach with artificial intelligence can predict a rise in toxic algae weeks earlier than the microscope method.
Intelligence
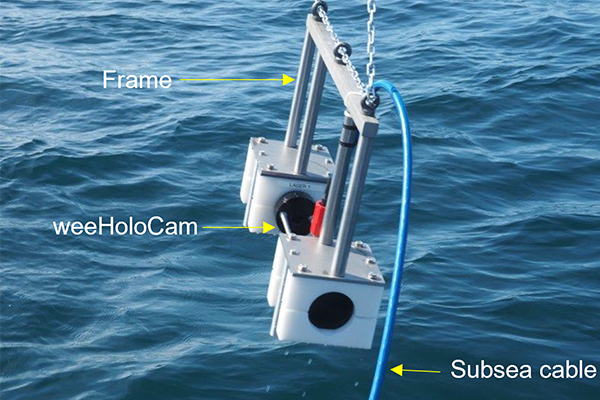
Could holographic cameras and AI technology lead to an early warning system for sea lice in the ocean?
Researchers are exploring the use of underwater holographic cameras and artificial intelligence technology to identify sea lice in the ocean.

Intelligence
Can artificial intelligence help solve sturgeon farming riddles in Japan?
A collaborative initiative in Japan explores at how artificial intelligence could make sturgeon farming more predictable and caviar supplies steadier.
Innovation & Investment
New artificial intelligence technology can detect early stress symptoms in farmed shrimp
A new artificial intelligence-based computer vision system can count and measure shrimp with up to 95 percent accuracy.



