
Hatchery, nursery production of freshwater prawns in temperate climates
The operation of a freshwater prawn hatchery in temperate climates presents a variety of challenges not found in the traditional greenwater or flow-through systems.
Research has been directed toward developing compound microdiets to ameliorate variability and poor nutritional quality of live food.

The operation of a freshwater prawn hatchery in temperate climates presents a variety of challenges not found in the traditional greenwater or flow-through systems.

Excitement about the potential farming of freshwater prawns in the United States has persisted for almost five decades but has yet to materialize.
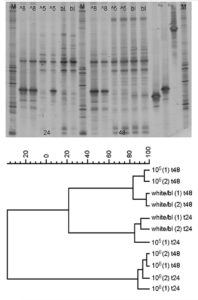
Probiotics for marine larviculture offer an alternative to the prophylactic use of antibiotics in aquaculture, which may lead to drug-resistance.
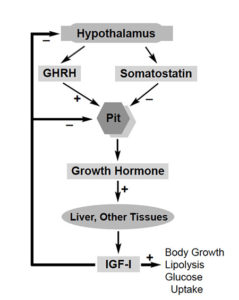
The enhancement of growth rate is a particularly important economic parameter, as it can significantly reduce the time required to produce market-size fish.

Study shows that increasing the dietary lipid level affected the lipid composition of shrimp by increasing lipid deposition in hepatopancreas and muscle tissue.

Spot histamine testing does not assure there are no histamine fish in the system, but does let suppliers know that handling procedure are double-checked.

Of all the issues important to shrimp nutrition, the reduction of feed cost with concomitant increased feed performance are most desirable.

HACCP plans bring the benefits of quality assurance, documented chain of custody, monitoring and inputs and better supervision of employee actions.

Authors carried out a series of experiments at and around Central Luzon State University designed to determine optimal feeding strategies for tilapia.
The Malaysian or giant freshwater prawn can be marketed live, chilled, or frozen. However, farmers face constraints regarding meat quality deterioration.
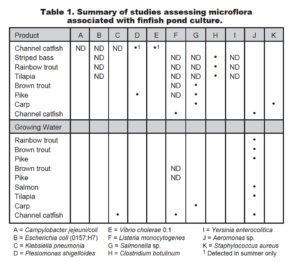
The microbial flora of farmed seafood products, particularly the microorganisms considered human pathogens, are important to individuals and agencies.

The amount of cottonseed meal that can be included in fish diets depends mainly on its levels of free gossypol and available lysine.

Atlantic halibut juveniles fed artemia in the larval stage often exhibit insufficient pigmentation and lack proper eye migration.

Numerous environmental, social and economic advantages support the expansion of euryhaline shrimp and fish production away from coastal environments.

The regulation of antibiotic use aims to guarantee the safety and efficacy of the drugs for the animals treated and protecting the health of consumers.