
Tilapia show immunization response against Ich
In research on alternatives to formalin treatment to control Ich infestation, the authors performed a study that compared the immune responses of Nile tilapia and red tilapia against the parasite.
Although concerns for the animal welfare of food animals are currently highest in the United Kingdom and European Union, they are also growing in other parts of the world.

In research on alternatives to formalin treatment to control Ich infestation, the authors performed a study that compared the immune responses of Nile tilapia and red tilapia against the parasite.

A study demonstrated that market-size shrimp can be profitably produced with zero water exchange in intensive raceways. The reuse of water that served for an earlier nursery study allowed the immediate establishment of a healthy microbial community in the grow-out study.
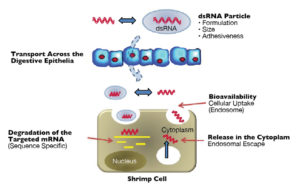
Therapeutics to harness an active RNA interference (RNAi) response in shrimp and protect against viral diseases could provide benefits to aquaculture.

As the demand for aquaculture products increases, so does the search for environmentally friendly alternatives to antibiotics. Alternatives to antibiotics include dietary prebiotics, probiotics and synbiotics.

In China, fleshy shrimp have had much higher market value than other shrimp species. China’s aquaculture scientists and fishery agencies have therefore worked closely with shrimp farmers to rebuild the farming industry for F. chinensis.

Although still being refined, the IMNV challenge method developed at the University of Arizona has shown promise as a tool to measure resistance in selected family lines of L. vannamei.

Although the application of selective breeding and genetics can yield dramatic results, the use of genetically improved stock varies widely among aquaculture sectors. Virtually all Atlantic salmon and rainbow trout producers use improved stock, while use of genetically improved tilapia varies widely.

Recirculating aquaculture systems have properties that can mature and stabilize the microbial community, creating a more benign bacterial flora in larval tanks.

The objective of a contingency plan is to quickly recover production through rapid initial response and effective implementation of biosecurity measures. Such plans depend on whether the detected pathogen or disease is exotic or endemic, its potential economic impacts and whether it is to be eradicated.

The development of an effective biosecurity plan requires full understanding of facility design and operations, and knowledge of the animals’ health status and the transmission modes of pathogens in order to identify the risks and define meaningful measures.

Biofloc technology provides high productivity, low feed-conversion ratios and a stable culture environment. Also, with viral problems and rising costs for energy, biofloc technology can help deliver sustainable production at lower cost.

Environmental and fish health problems have affected Chile’s salmon farmers since 2004. As production ramped up, 2006 saw an increase in sea lice that reduced output. In 2007, infectious salmon anemia spread across the farming region and quickly cut production.

Tilapia quickly reach sexual maturity in culture, and unless controlled, the fish reproduce and offspring compete for food. All-male culture of tilapia is preferred because of their fast growth and larger average size.

For two years of data, the effects of management, season, stocking density and salinity on the incidence of disease in northeastern Brazil’s shrimp farms were found to be highly significant.

The effective control of tilapia health depends on integrated management that considers all factors, including species, the environment, pathogens present and farm management practices.