
Sulfides alter aquaculture pond pH, can be toxic
Ponds constructed where soils contain sulfides can have problems with low pH in culture water. Liming can be an effective emergency measure.

Effluent effects from aquaculture ponds
In general, lower-intensity pond and cage farming tends to discharge higher overall pollution loads in farm effluents than closed aquaculture systems.

Study identifies maximum holding times for water samples
Although pond water samples collected to measure water quality are often held on ice, the values of some common variables in the samples can vary over time.

Copper treatments control phytoplankton
Copper sulfate is widely used as an algicide in ponds and other aquatic systems. Although copper quickly disappears from pond water, cupric ions can be harmful to aquatic animals.

Measuring water flow
Water flow within channels can be measured using the float method or calculated using rating curves that project water velocity based on a series of finite measurements.

Secchi disk visibility: Correct measurement, interpretation
It would be difficult to find a pond aquaculture worker who has not measured Secchi disk visibility or at least seen someone measure it.

Organic matter in pond bottom sediment
Organic matter – including fertilizers, unconsumed feed and feces of culture animals – settles to pond bottoms, often with a negative impact on water quality.
Zeolite ineffective as pond treatment
Zeolite is used in industry for water softening and as media for molecular sieves but has no real benefit for aquaculture in ammonia removal.

Specific conductance: An alternative salinity measurement
Water's ability to conduct electricity increases with the total concentration of dissolved ions. Measuring conductivity helps estimate salt content of water.

Land and water use issues in aquaculture
It behooves us to understand land and water use issues and understand the differences between aquaculture and traditional agriculture.

Water quality standards: pH
The pH of shrimp pond water is influenced by source water, pH and acidity of bottom soil, shrimp culture inputs and biological activity.
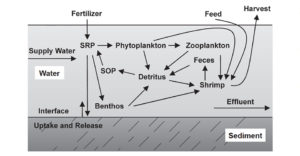
Water quality standards: Total phosphorus
Two nutrient elements, nitrogen and phosphorus, are responsible for eutrophication in most instances. Phosphorus is usually the key factor.
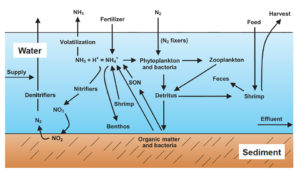
Water quality standards: Total Ammonia Nitrogen
For seawater or brackish water aquaculture management, the salicylate method is best for total ammonia nitrogen analysis.

Formulating standards for effluent management
A major environmental consideration in shrimp farming is the negative impacts of pond effluents on coastal water quality.

Water use in aquaculture
Because aquaculture is a water-intensive endeavor, conservationists have begun to inquire about the possibility of excessive water use in aquaculture.

Farm effluent during draining for harvest
Settling basins seem to be the only practical means of treating effluents released during harvest at small or large shrimp farms.

Water composition and shrimp pond management
Natural waters have a very complex chemical composition and may contain almost any substance found in the atmosphere, in the Earth’s crust, or in living organisms.

Round peg in a square hole: Aeration in a square shrimp pond
Appropriate site selection, design and management are fundamental factors that contribute to the success or failure of a shrimp farm.
