Coastal Zones Research Institute spearheads efforts to coordinate research, extension and commercialization initiatives
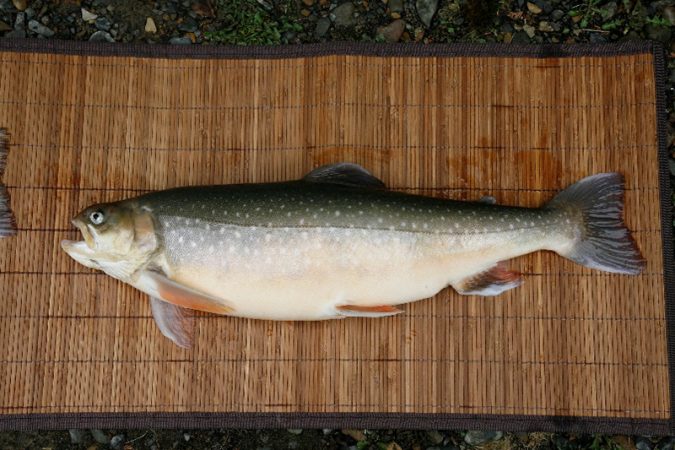

In Canada, there is a growing interest in aquaculture production, which represents about 15 percent and 20 perceny of the total seafood volume and value, respectively. Salmonids – including Atlantic salmon, trout, steelhead and Arctic charr – represent the most cultivated aquatic organisms in the country. The Artic charr (Salvelinus alpinus) is a cold-water fish species that grows well at the northerly latitudes in Canada and northern United States, as well as other Nordic countries such as Iceland, Sweden and Norway.
Farming and production
There are no consistent statistics on Arctic charr farming, but the global production of the fish is estimated at less than 10,000 metric tons (MT). Iceland is the top producer with more than 3,500 MT produced per year.
Since 2006, the Monterey Bay Aquarium’s Seafood Watch considers farmed Arctic charr from Iceland, the United States and Canada as a “best choice” for consumers, because its farming is done in environmentally friendly ways. Also, Arctic charr products constitute a market niche, with price sometimes twice as high as that of its salmon counterparts.
Artic charr farming is gaining momentum worldwide. For instance, Aqua-Spark, a global investment fund dedicated to aquaculture, recently invested in two Arctic charr farms, Urban Organics in the United States and Matorka Holdings AG in Iceland; the former is planning to produce a few hundred metric tons, while the latter is planning to produce over 3,000 MT of Arctic charr per year.
Over the last two decades, scientific and technical efforts have been deployed in Canada to characterize the Artic charr strains collected from the wild by government agencies, to accelerate their domestication, to improve their growth potential through selective breeding and to develop environmentally friendly husbandry techniques. The three Arctic charr strains currently farmed in Canada are the Fraser, Nauyuk and Tree River strains, which originated from the Fraser River in Labrador, Nauyuk Lake in Nunavut, and Tree River system in Nunavut, respectively.

In addition, despite the strict regulatory systems and the heavy government bureaucracy facing the aquaculture industry in Canada, the Canadian Arctic charr producers have managed to develop this sector to a financially profitable level, thanks to the remarkable success achieved in the selection and improvement of the Canadian strains of Arctic charr, the acquisition of extensive hands-on experience in the husbandry of this fish species, and the mastering of sophisticated and efficient rearing systems such as recirculating aquaculture systems.
Despite all these efforts, the current annual production of farmed Canadian Arctic charr, which can be estimated at about 500MT, is not enough to satisfy the increasing national and international consumer’s demand.
Pan-Canadian project with many stakeholders
In order to spur the sustainable growth of Arctic charr aquaculture in Canada, the Coastal Zones Research Institute Inc. (CZRI) organized the international workshop on Artic charr farming in 2011 in Moncton, New Brunswick, Canada. As the result of this workshop, CZRI with its partners launched the pan-Canadian project on “Aquaculture Development and Profitable Commercialization of Arctic charr in Canada,” which started in 2014. This five-year project is led by CZRI and is mainly funded by the Atlantic Canada Opportunities Agency (ACOA) of the Government of Canada through the Atlantic Innovation Fund.
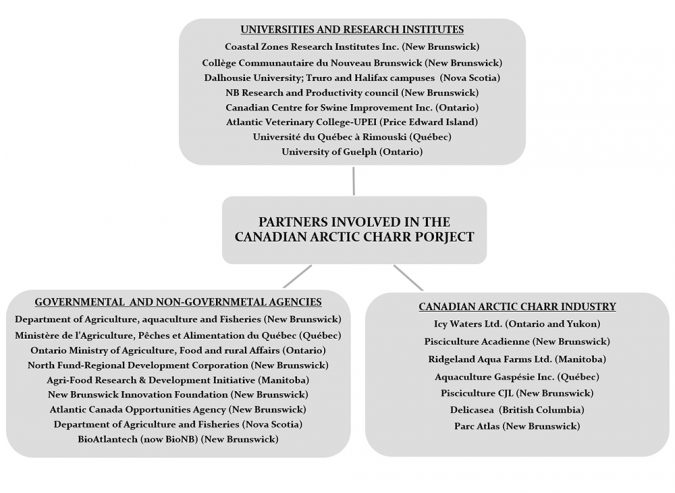
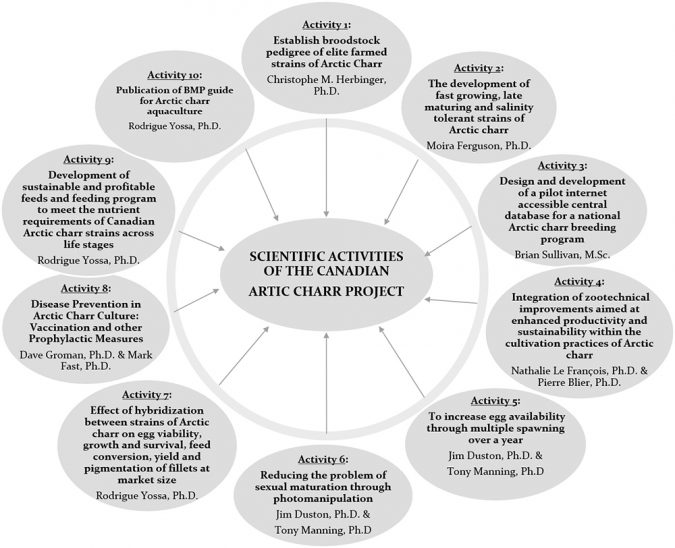
The goal of this project is to create a synergy among the stakeholders of the Arctic charr farming in Canada, through coordinated research, extension and commercialization initiatives across the country. The partners involved in the Arctic charr project include governmental and non-governmental agencies, universities and research institutes, and the Canadian Arctic charr producers, all from eight provinces and territories of Canada (Fig. 1). The 10 scientific activities of this project include both fundamental and applied research on genetics, disease and health management, nutrition, husbandry and best aquaculture practices (Fig. 2).
Each scientist works in partnership with an industrial partner and conducts research both on-station and on-farm. In this manner, scientific research is focused on the practical issues in the fish farms, and any new technologies developed through this farmer-scientist research partnership are directly applicable to the participating farm, before being shared with all the Arctic charr producers and government agencies involved in the whole project.
Perspectives
So far, the activities of this pan-Canadian Arctic charr project are progressing well, and all the project stakeholders gather once a year. During this annual meeting, the scientific progresses are shared with all the project stakeholders, practical aquaculture experiences are shared between the producers, and CZRI gives an update on the project execution, monitoring and controlling.
Thanks to this project, the participating producers are exposed to cutting-edge science and technologies, which help them improve their farm practices. Also, new Arctic charr farms are emerging in Canada, mostly in the Provinces of Manitoba and New Brunswick, following the model of the existing successful farms involved in this project.
Using this farmer-scientist participatory research approach, this Arctic charr project will ultimately significantly help to realize the aquaculture potential of this highly-appreciated fish species in Canada.
Author
-
Rodrigue Yossa, Ph.D.
Arctic Charr AIF Project Leader
Coastal Zones Research Institute Inc.
232B avenue de l’Église, Shippagan, N.B., E8S 1J2, Canada
www.irzc.umcs.ca
[97,99,46,115,99,109,117,46,99,122,114,105,64,97,115,115,111,121,46,101,117,103,105,114,100,111,114]
Tagged With
Related Posts

Health & Welfare
Novel air-based system transfers large salmon during harvest
To evaluate the application of an air pressure-based transport method within a recirculating aquaculture system, the authors performed testing with harvest-size salmon at The Conservation Fund Freshwater Institute.

Innovation & Investment
Matorka aims to unearth innovation with Arctic charr
A new and ambitious Iceland company is about to construct what it claims will be the world’s largest land-based salmonid farm. What sets Matorka’s Arctic char farm apart is its ability to tap into natural resources unique to the island nation.

Intelligence
Off the Knife with Ned Bell, Vancouver Aquarium
We delve deeper into the foodservice industry’s engagement with sustainable seafood and aquaculture by talking to Ned Bell, the Vancouver Aquarium’s new executive chef. He continues to call on his Canadian culinary comrades to learn more about seafood, then help educate consumers.

Responsibility
In Canada, salmon farmers building social license with First Nations
After some rocky times, ties between B.C. salmon farmers and First Nations, have improved in recent years. Band members report consistent employment, royalties and improved quality of life. “We need aquaculture around,” says one fishing company owner.


